This isn’t a “magic bullet,” it’s a buckshot aimed at a barn door.
Yes, I think sugar and empty calories , and the associated hyperinsulinemia are the bane of anyone with obesity or any sort of hyperplastic fat tissue disorder. And yes, this is the worst type of evidence to support such a stance, but when you’ve got lemons, well…
, and the associated hyperinsulinemia are the bane of anyone with obesity or any sort of hyperplastic fat tissue disorder. And yes, this is the worst type of evidence to support such a stance, but when you’ve got lemons, well…
Make no mistake, diabulemia may as well be spelled DIE-abulemia. It’s not a laughing matter. But yeah, well, lemonade, etc. So here it goes
Diabulemia
Type I diabetics have low insulin and are lean; type II diabetics have high insulin and are not. Insulin injections in either population promotes hyperplastic fat growth. Sounds scary, right? It is:
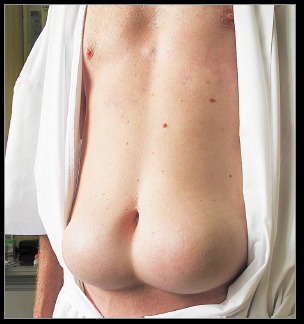
This poor soul unfortunately restricted his insulin injections to only two sites. Make all the jokes you want, but the effect is obvious… this is happening everywhere in hyperinsulinemic heavyweights (not just two specific sites).


So what do Type I’s do when they want to lose some fat mass? Stop jabbing themselves with insulin. Unfortunately, it’s really that simple. Type II’s and anyone with excess or hyperplastic fat tissue can do the same with low carb or keto, although this would be a great benefit to their overall health. But for Type I’s… not so much – they need insulin to prevent the horrific manifestations of ketoacidosis, which includes but is not limited to: death.
Type I’s are hyperglycemic because of low insulin; insulin therapy prevents diabetic ketoacidosis, a deadly condition . But for those who simply choose to selectively reduce their insulin dosage, they: 1) don’t die; 2) lose fat; and 3) get hyperglycemic and incur all the damage that ensues (retinopathy, nephropathy, neuropathy). Furthermore, they’re walking on thin ice – DKA is lurking. It is just as stupid yet more dangerous than using tapeworms to lose weight.
. But for those who simply choose to selectively reduce their insulin dosage, they: 1) don’t die; 2) lose fat; and 3) get hyperglycemic and incur all the damage that ensues (retinopathy, nephropathy, neuropathy). Furthermore, they’re walking on thin ice – DKA is lurking. It is just as stupid yet more dangerous than using tapeworms to lose weight.

Type II’s are hyperglycemic because of insulin resistance; a condition that is pathologically neutered via carbohydrate restriction. Type I’s who reduce insulin injections to decrease fat mass are doing just as much damage as Type II’s who DON’T reduce carbohydrate intake.
Diabulemia is akin to an eating disorder. Biologically, the lack of insulin allows fat to be released from adipose tissue with gravitas, and it prevents glucose from being stored in any meaningful capacity. You’re literally pissing calories here, burning ’em like crazy there; all of which is a helluva lot easier than “eating less moving more” … which is why diabulemics do it (because they have the option [unlike the rest of us]). Diabulemia is good from a fat loss perspective, but will most definitely contribute to severe and possibly deadly complications down the line. Carbohydrate restriction, however, is a win-win-win… (for everyone except The Man, so perhaps it’s a win-win-win… fail)
This isn’t a “magic bullet,” it’s a buckshot aimed at a barn door.
Humans aren’t big rats, but here it is again, anyway:
Leptin deficiency causes insulin resistance induced by uncontrolled diabetes (German et al., 2010)
I’m ignoring the brunt of this paper and only focusing on the positive control groups. [Positive controls… meaning they were included because they would definitely exhibit the expected response.]
Force rats into a state of diabulemia, and their insulin levels plummet, blood glucose soars, and they become ravenously hungry (open squares in the graphs below).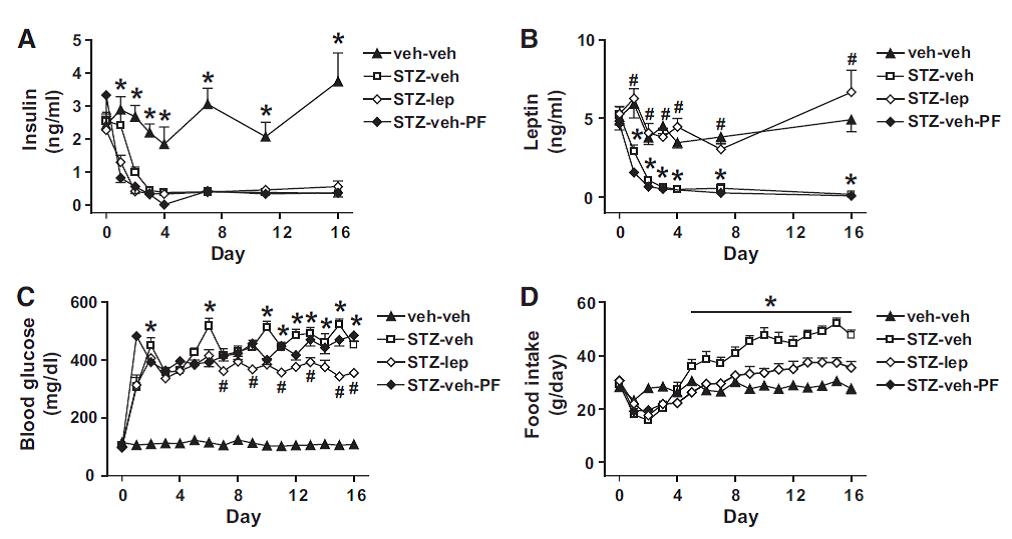
But lo and behold, fat mass atrophy ->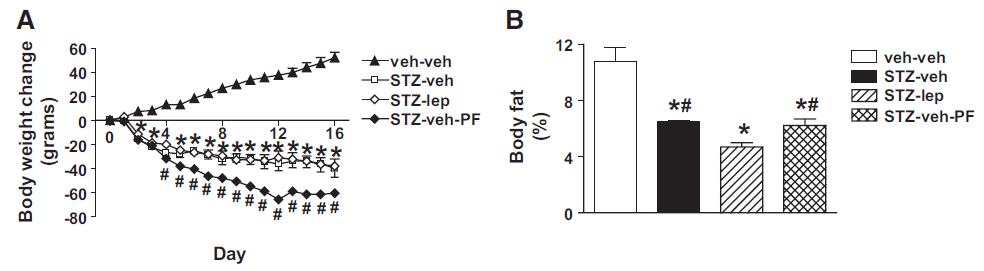
Eat less move more? Well, they certainly didn’t “eat less…” (see above) … and:
nor were they “moving more.” Low insulin seems to have a way to bypass that whole “eat less move more” thing (eg, Metabolic rate per se).
Throwing the baby out with the bathwater works if the baby is fat and the bathwater is insulin. (no, not a fat baby.)
calories proper