So, we have another “high protein” weight loss study (Smith et al., 2016). Or really, a “low (0.8 g/kg) vs. moderate (1.2 g/kg) protein weight loss study.” In brief, it took ’em about 6 months to lose 10% of their starting body weight, then were given 4 weeks of weight stability before “after” measurements were taken.
Important: this was not a contest to see who would lose more weight; they kept going and adjusting food intake until both groups lost 10%. Not really ad lib, but otherwise a good study design imo. The intervention was relatively weak (eg, protein 0.8 vs. 1.2 g/kg), but on the plus side, that’s realistic and very “do-able.” If you’re interested in super-high protein diets (3-4 g/kg), check out research by Jose Antonio.
Big yet not unexpected finding: the low protein group lost about twice as much muscle than the normal protein group.
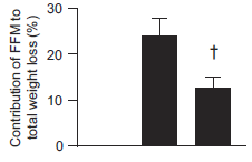
The isocaloric normal protein group lost more fat and less muscle than the low protein group.
But then everyone freaked out because the low protein group experienced a significant improvement in muscle/liver insulin sensitivity whereas the normal protein group didn’t:
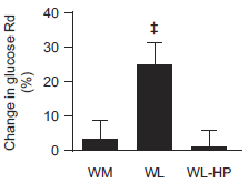
-The headlines were hilarious, like, “high protein makes weight loss not work anymore.”
-Then some critics jumped the shark and blamed it on “liquid calories,” because whey protein shakes are totes non-Paleo, and #JERF.
-TBH, I found more interesting the changes in adipose insulin sensitivity…
The normal protein group had the most insulin sensitive adipose of all groups… yet they lost more fat mass despite eating just as much or even slightly more than the other groups.
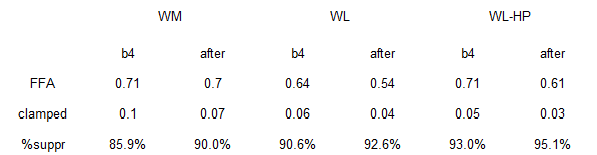
Does this mean they’re doomed to regain the weight? I don’t think so, as high dietary protein is one of the strongest predictors of weight loss success long-term.
HERESY! the low protein group had: 1) lower basal insulin than the normal protein group; 2) lower adipose insulin sensitivity; 3) ate less (NS); yet lost less fat mass.
In other words, the normal protein group had higher basal insulin, more insulin sensitive adipose tissue, and slightly higher food intake (NS). According to the insulin model, they should’ve lost less fat mass than the low protein group, but they didn’t.
Is this another chink in the armor of the insulin model?
The truth seems to be: people lose weight on both LC and LF diets by giving up junk food. On LC, this is accomplished by giving up carbs; on LF, this is accomplished by switching to better carbs. Some people adhere better to one diet or the other. Maybe insulin sensitivity has something to do with it.
Insulin from high protein: not bad?
Insulin from good carbs: not bad?
Junk food: no bueno.
So maybe just maybe it’s not just ze insulin…
Back to the protein…
This was not sorcery; it’s been seen before in a variety of different paradigms: dietary protein has a profound impact on nutrient partitioning.
Yes, even when it’s liquid calorie insulinogenic whey protein isolate bro-shakes.
Yes, even when it’s not crazy-high levels of protein… seriously, 1.2 g/kg is not “high”
+ + + + + + + + + +
Past blog posts on [the non-sorcery of] dietary protein:
Holiday feasts, the freshman 15, and damage control
Dietary protein, ketosis, and appetite control.
Nutrient Partitioning: …a *very* high protein diet.
Protein “requirements,” carbs, and nutrient partitioning
Cyclical ketosis, glycogen depletion, and nutrient partitioning
Meal frequency, intermittent fasting, and dietary protein
Muscle growth sans carbs
+ + + + + + + + + +
For full access to all articles and much more (or if you just like what I do and want to support it), become a Patron! It’s three bucks a month and there are many other options. Sign up soon because there are only a limited number of spots left at the $3 level. It’s ad-free and you can cancel if it sucks ????
Also, I’m open to suggestions, so please don’t hesitate to leave a comment or contact me directly at drlagakos@gmail.com.
Affiliate discounts: if you’re still looking for a pair of hot blue blockers, Carbonshade is offering 15% off with the coupon code LAGAKOS and Spectra479 is offering 15% off HERE. TrueDark is running a pretty big sale HERE. If you have no idea what I’m talking about, read this then this.
20% off some delish stocks and broths from Kettle and Fire HERE.
If you want the benefits of ‘shrooms but don’t like eating them, Real Mushrooms makes great extracts. 10% off with coupon code LAGAKOS.
calories proper
Become a Patron!
Save
Save
Save
Save
Save
Save
Save
Save
Save