Recent findings and current developments: where do we stand today?
Great “Tl;dr:” figure ->
There is most definitely a multi-level bidirectional relationship between mood disorders and diet/lifestyle habits. Can diet cause or cure mood disorders? Can mood disorders cause you to eat/behave a certain way? Yes, yes, and yes. #Context.
That said, diet interventions present a unique and potentially useful treatment avenue for mood disorders.
Mood disorders are a significant source of mental capital loss with high rates of treatment resistance, in part, because we have no clue about the causes, full influence of their spectrums, or how exactly the effective pharmacotherapies work.
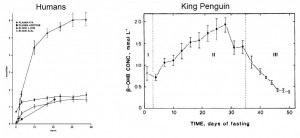
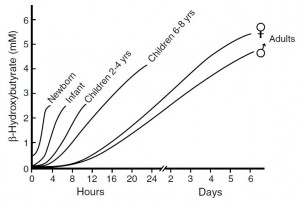
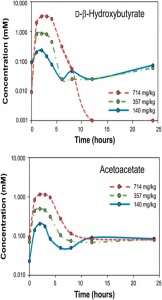
The ketogenic diet: why it should be explored ->
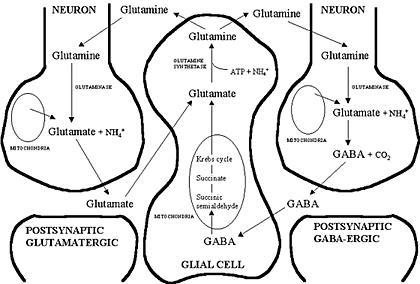
- Ketogenic diet has profound effects in multiple targets implicated in the pathophysiology of mood disorders, including glutamate/GABA transmission, monoamine levels, mitochondrial quantity and quality, neurotrophism, oxidative stress, insulin signaling, inflammation, etc., etc…
- Benign dietary ketosis is a very exclusive diet, immediately cutting out many of the potentially offensive foods.
- Malign dietary ketosis, while still technically ketosis, is full of unhealthy n6- and trans fat-rich oils, insufficient protein and fibre, etc. It’s basically the bacon-wrapped cheese dog version of keto.
Domains of depressive symptomatology of interest: anhedonia, rumination, suicidality, sleep disruption, appetite dysregulation, among others.
In this context, it may be perfectly legitimate to supplement a low carb diet with exogenous ketones or coconut oil.
For the rest of this article and more, head over to Patreon! Five bucks a month for full access and there are many other options. It’s ad-free and you can cancel if it sucks 🙂
If you’re interested in setting up consultations, email me: drlagakos@gmail.com.
Affiliate links: join Binance and get some cryptoassets or download Honeyminer and get some Bitcoins for free! And now you can mine Bitcoin from your Chromebook!
Still looking for a pair of hot blue blockers? Carbonshade and TrueDark are offering 15% off with the coupon code LAGAKOS and Spectra479 is offering 15% off HERE. If you have no idea what I’m talking about, read this then this.
20% off some delish stocks and broths from Kettle and Fire HERE.
If you want the benefits of ‘shrooms but don’t like eating them, Real Mushrooms makes great extracts. 10% off with coupon code LAGAKOS. I recommend Lion’s Mane for the brain and Reishi for everything else.
Join Earn.com with this link.
Start your OWN Patreon campaign!