Symptoms: fatigue, cold-intolerance, hair loss, decreased libido, constipation… sound familiar?
Hypothyroid-like symptoms occur relatively frequently during times of rapid fat loss, and this may be at least partially dependent on diet quality. Another component is the fact of being in an energy deficit, but this is difficult to evade on a weight loss diet.
Tl;dr: large energy deficit = hypothyroid-like symptoms.
Food choices and diet quality is important, too.
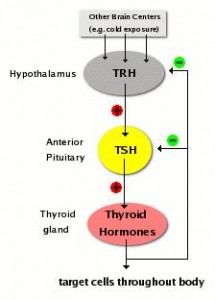
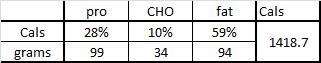
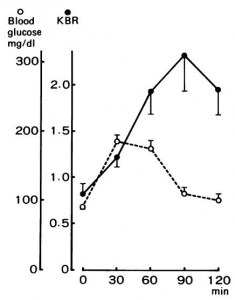
The negative impact of low calorie diet-induced weight loss on thyroid biology and energy metabolism is well established, but this figure from Agnihothri and colleagues sums it up rather nicely (2014):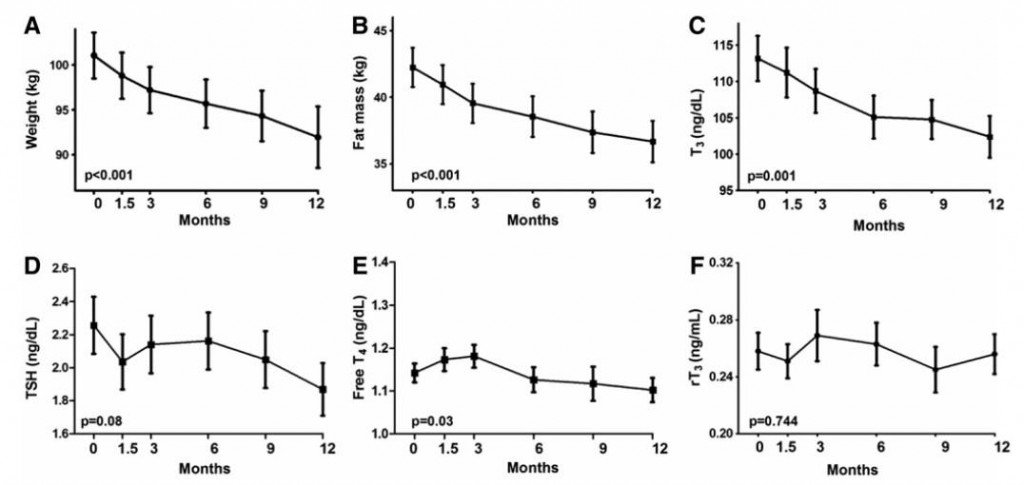
Rapid fat loss causes a decline in TSH and T3.
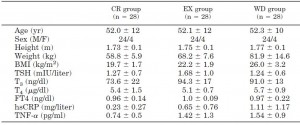
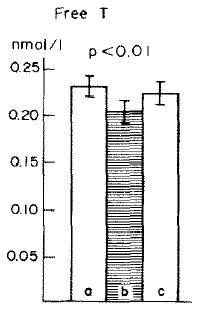
And in this study on long-term calorie restriction (3-15 years), a similar phenomenon occurred (Fontana et al., 2006). However, TSH was normal (unlike in Agnihothri’s study), possibly because they were not actively losing weight:
Note: calorie restricted diet had adequate protein… low T3 because they’re weight-reduced and hypoleptinemic, and normal TSH because they’re not actively losing weight.
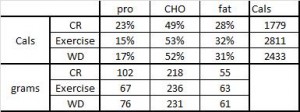
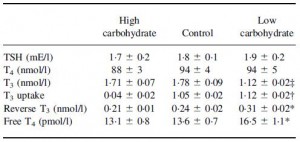
But then there’s this study, which shows active weight loss does not necessarily cause reduced TSH levels, if the diet is ketogenic (Yancy et al., 2005):
Also, this study showed reduced T3 after 11 days on a ketogenic diet, but it didn’t impact TSH or resting energy expenditure , suggesting no hypothyroid-like symptoms (Bisschop et al., 2001):
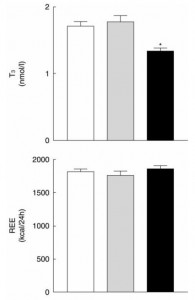
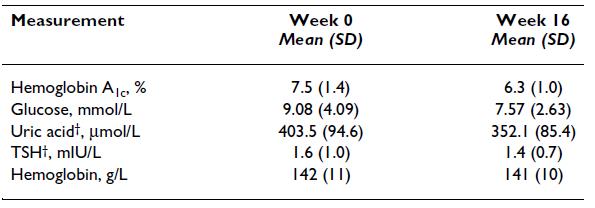
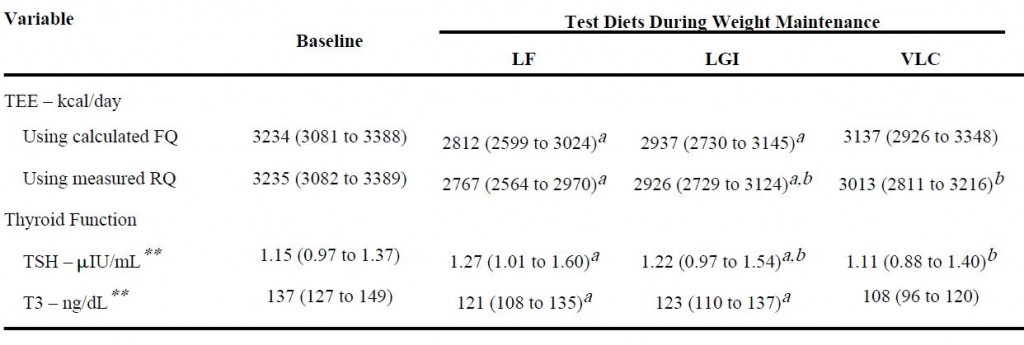
And lastly, from the [notorious] Ebbeling study:
Low TSH and low T3, but highest energy expenditure in weight-reduced patients on very low-carbohydrate diet.
Summary
Agnihothri: Low calorie diet-induced active weight loss: low T3 and low TSH; probably low energy expenditure and hypothyroid-like symptoms.
Yancy: Ketogenic diet, active weight loss: normal TSH.
Fontana: Weight-reduced, weight-stable (CR): low T3, normal TSH.
Bisschop: Ketogenic diet, weight-stable (11 days): low T3, normal TSH, and normal energy expenditure (indicative of no hypothyroid-like symptoms)
Ebbeling: Very low-carbohydrate diet, weight-stable (4 weeks): low T3, low TSH, normal energy expenditure (indicative of no hypothyroid-like symptoms).
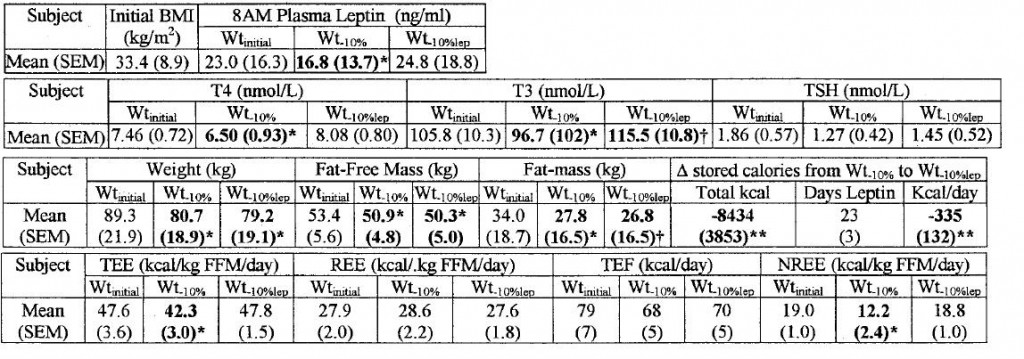
In all of the above studies, leptin mirrored body fat. And all of the old Rosenbaum & Leibel studies showed the reduction in thyroid function after low calorie diet-induced weight loss could be repaired with leptin treatment. Their 2002 paper had it all (Rosenbaum et al., 2002)… replacing leptin levels to pre-weight loss levels, which required roughly 3 mg/d, completely restored thyroid levels and energy expenditure:
Carbohydrate restriction appears to throw a wrench in the gears.
We also know from rodent studies that excess carbohydrates, particularly fructose, can induce leptin resistance. Perhaps by improving leptin sensitivity, carbohydrate restriction attenuates some of the hypothyroid-like symptoms associated with an energy deficit. This would explain the findings of Bisschop’s and Ebbeling’s studies, and would be in line with the known impact of carbohydrate restriction on lowering plasma triacylglycerols, and the theorized (and somewhat controversial) association between high triacylglycerols and low leptin sensitivity.
If you’re on a weight loss diet and are experiencing cold intolerance, fatigue, low libido, or any other hypothyroid-like symptoms, consider either upping the calories or lowering the carbs (or this?).
If you like what I do and want to support it, check out my Patreon campaign!
UPDATED Affiliate links: still looking for a pair of hot blue blockers? Carbonshade is offering 15% off with the coupon code LAGAKOS and Spectra479 is offering 15% off HERE.
If you have no idea what I’m talking about, read this then this.
20% off some delish stocks and broths from Kettle and Fire HERE.
If you want the benefits of ‘shrooms but don’t like eating them, Real Mushrooms makes great extracts. 10% off with coupon code LAGAKOS. I recommend Lion’s Mane for the brain and Reishi for everything else.
Join Earn.com with this link. Get free magical internet money!