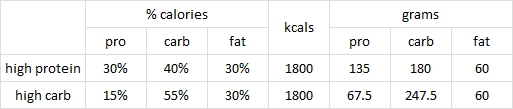Remission of pre-diabetes to normal glucose tolerance in obese adults with high protein versus high carbohydrate diet: randomized control trial (Stentz et al., 2016)
n=12/group
Duration = 6 months
Diet: all food provided. Mucho gusto!
Critique #1: if my calculations are correct, we’re comparing low protein (0.675 g/kg) to adequate (1.35 g/kg) (not “high”).
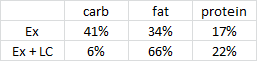
The diets were decent:
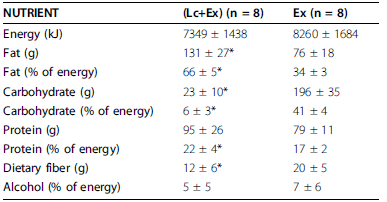
Results:
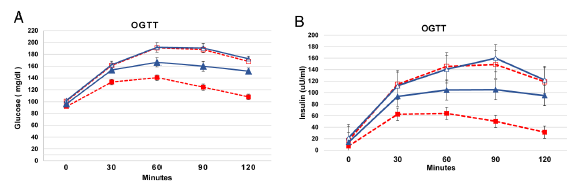
Author’s conclusion was that this was due to high protein alone, but I’d say it was at least partially due to weight loss. BOTH groups lost weight and improved insulin sensitivity. Statistically significant in both groups.
Glucose (A) and insulin (B) in response to a 75g OGTT (red is high protein, blue high carb):
I still say weight loss was the primary driver, but must concede, however, that protein did have a little magical effect: high carb group actually lost slightly more weight, but insulin sensitivity improved more in the high protein group. The high protein magic: reduced insulin secretion yet still greater reduction in glycemia.
Well, maybe not magic…
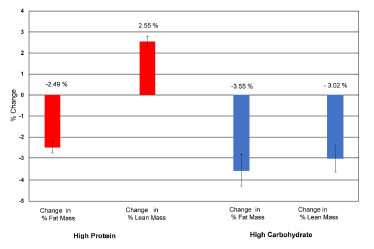
Despite having more insulin, high carbers lost slightly more fat mass but way more muscle. THAT’s high protein magic lol
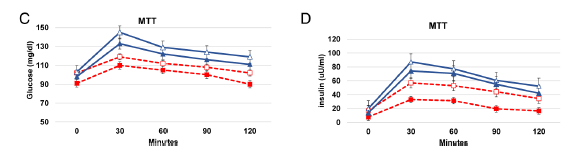
However, the meal tolerance tests show a slightly different trend:
We expect glucose and insulin excursions to be greater in HC (blue), because they had a high carb meal whereas the HP group had a high protein meal. From this perspective, if we graphed the results as “change from time zero,” I think the reduction in glycemia from baseline to 6 months would be similar in both groups suggesting weight loss as bigger factor. We’d still give some props to high protein because it lowered glucose just as much despite having less insulin. High protein magic.
Note to self: gotta stop saying this was “high protein.” 1.35 g/kg is not “high,” seriously. But still, High protein magic haha
Oh and one other thing, high protein usually induces greater weight loss:
Randomized trial on protein vs carbohydrate in ad libitum fat reduced diet for the treatment of obesity (Skov et al., 1999)
High protein vs high carbohydrate hypoenergetic diet for the treatment of obese hyperinsulinemic subjects (Baba et al., 1999) (not ad lib)
Comparison of high-fat and high-proein diets with a high-carbohydrate diet in insulin-resistant obese women (McAuley et al., 2005)
The effect of a low-fat, high-protein or high-carbohydrate ad libitum diiet on weight loss maintenance and metabolic risk factors (Claessens et al., 2009)