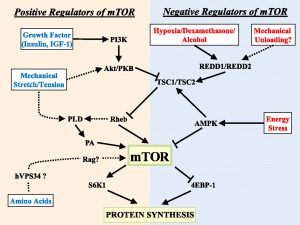
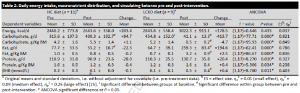
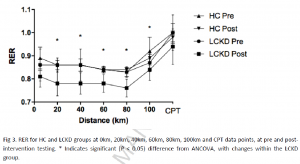
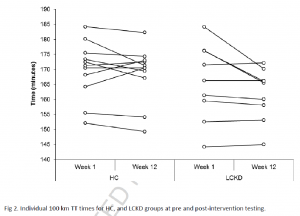
Alternative title: keto isn’t muscle-sparing if you compare it to any remotely sensible control group.
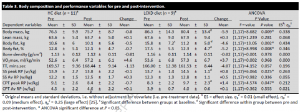
Exhibit A. Resistance training in overweight women on a ketogenic diet conserved lean body mass while reducing body fat (Jabekk et al., 2010)
The exercise intervention was resistance and progressive. The diet was ketogenic, confirmed by urinary ketones… of note, presence of urinary ketones is a better indicator of ketosis than any information about diet (although they were advised to start at <20g carb/d).
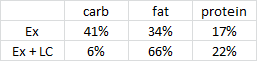
As per usual, the LC diet was higher in protein… but that wasn’t enough to induce skeletal muscle growth, even when combined with resistance exercise… worded another way, resistance exercise and more protein prevented ketogenic diet-induced muscle loss:

Neither group was instructed to restrict energy intake, but from the above graph it’s relatively safe to assume the LC diet counteracted exercise-induced hunger.
Confirmed:
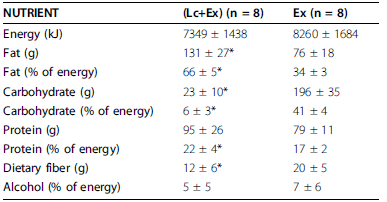
However, exercise-induced hunger isn’t conducive to fattening because the cause is exercise. I think.
Ketones may spare muscle during starvation, but not in the context of regular people eating a ketogenic diet. Otherwise, muscle mass would’ve increased in that study relative to the control group. Confounded by negative energy balance? Perhaps, but from where I’m standing, the LC diet did almost exactly what we expected: reduced food intake and induced a selective loss of fat mass. And exercise also performed as expected: increased muscle mass. In other words, if you want to gain muscle, you need calories, protein, and exercise. Keto provides no advantages in this context.
Exhibit B. The effect of weight loss by ketogenic diet on the body composition, performance-related physical fitness factors, and cytokines of Taekwondo athletes (Rhyu and Cho, 2014)
Keto dieters got 33% more protein (40% vs. 30%), and still managed to lose almost twice as much lean mass as non-ketogenic dieters.
 (figure from Suppversity)
(figure from Suppversity)
The participants were physically active, and thus likely fairly insulin sensitive, so this may be why those assigned to a ketogenic diet lost less body fat…
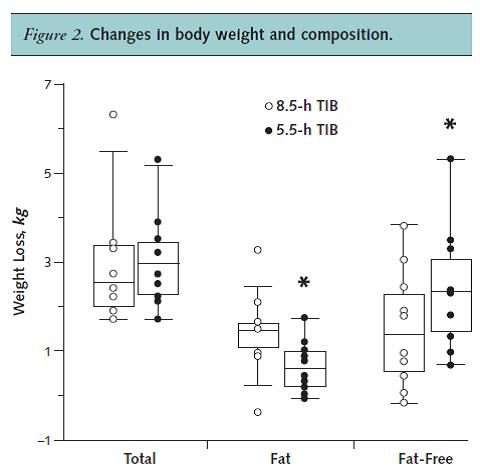
Exhibit C. Comparison of energy-restricted very low-carbohydrate and low-fat diets on weight loss and body composition in overweight men and women (Volek et al., 2004)
And in this study on sedentary insulin resistant folk, keto still wasted muscle (NS) despite more protein and calories:
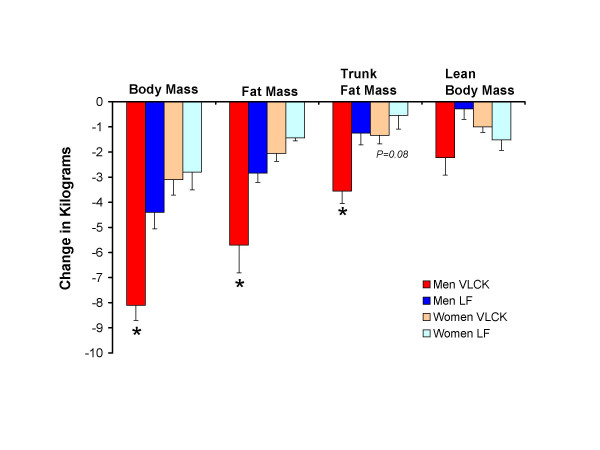
If you’ve been paying attention, this wasn’t unexpected.
Sedentary and overweight: more fat loss on keto.
Keto and sedentary: muscle loss.
Sleep well, get your circadian rhythms entrained proper — otherwise these efforts will give you a mere fraction of the benefits.
Other~
Protein + exercise works: Interactive effects of an isocaloric high-protein diet and resistance exercise on body composition, ghrelin, and metabolic and hormonal parameters in untrained young men: A randomized clinical trial (Kim et al., 2014)
Simply replacing carbs with fat, or resisting food for as long as possible after waking up and staring at your smart phone all night: doesn’t work.
#context
If you like what I do and want to support it, check out my Patreon campaign!
Affiliate links: still looking for a pair of hot blue blockers? Carbonshade is offering 15% off with the coupon code LAGAKOS and Spectra479 is offering 15% off HERE.
If you have no idea what I’m talking about, read this then this.
20% off some delish stocks and broths from Kettle and Fire HERE.
If you want the benefits of ‘shrooms but don’t like eating them, Real Mushrooms makes great extracts. 10% off with coupon code LAGAKOS. I recommend Lion’s Mane for the brain and Reishi for everything else.
calories proper
Become a Patron!
Save
Save
Save
Save
Save
Save
Save
Save
Save