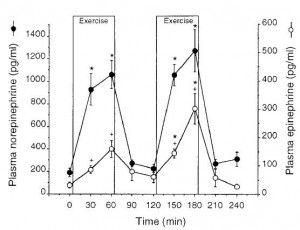
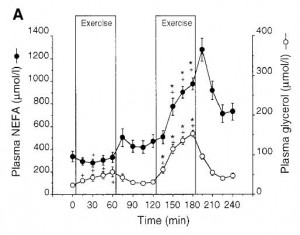
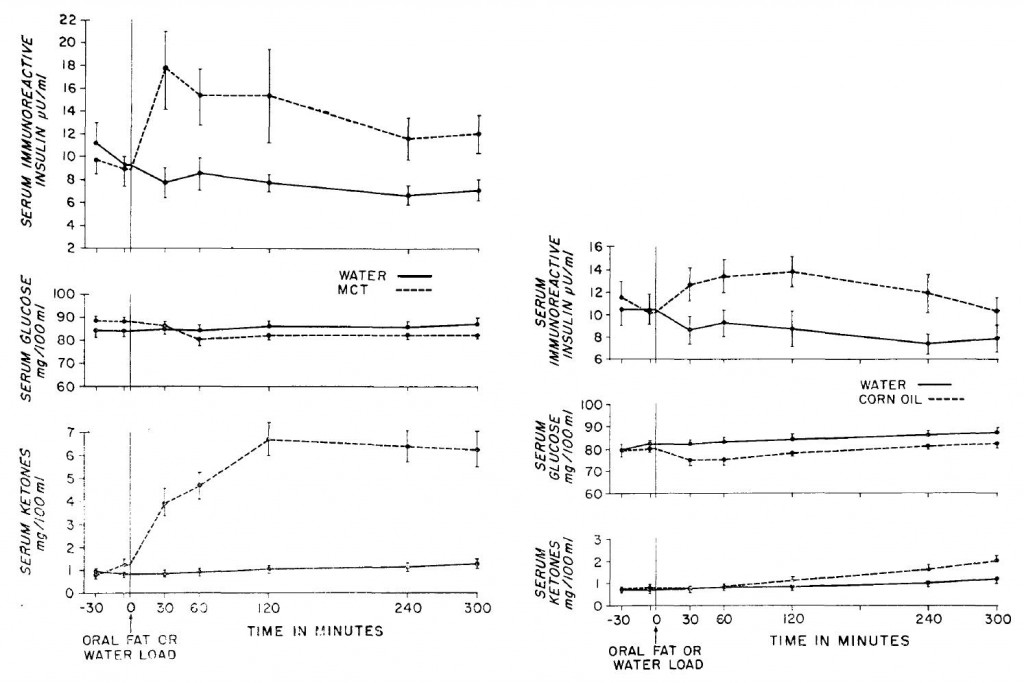
Switch an athlete from their standard carbohydrate-rich diet to a low carb ketogenic one and suddenly performance tanks. It is known. Give them a few weeks to adapt, however, and it recovers. This much was established for mainly endurance-related performance parameters by Steve Phinney and colleagues in the 1980’s (eg, Phinney et al., 1983). Then, along came Antonio Paoli, Dominic D’Agostino, and others who showed a similar phenomenon in gymnasts, a population that routinely exercises at higher levels of intensity (Paoli et al., 2012). Notably, in these studies the athletes were allowed adequate time to adapt to the new metabolic milieu – sometimes referred to as ketoadaptation. Three weeks appears to be the minimum amount of time required for ketoadaptation; ie, studies of shorter duration generally show: low carb = poor physical performance.
…which is why I was surprised to see this one:
Effects of a short-term carbohydrate-restricted diet on strength and power performance (Sawyer et al., 2014)
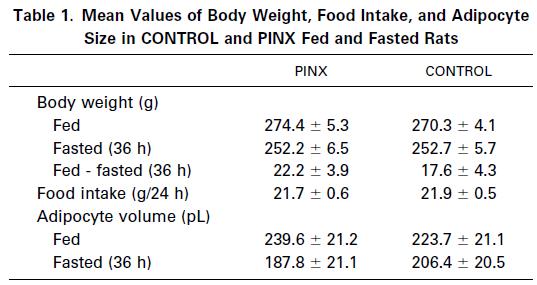
These researchers subjected ~30 strength-trained individuals to a battery of performance assessments before and after 7 days of a low carb [ketogenic] diet. Usually I would’ve stopped reading at this point because 7 days is too short. But there were some nuances in the way this particular study was designed which piqued my interest.