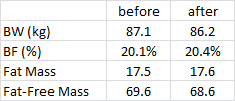This one has a bit for everyone.
Relationship of Insulin Dynamics to Body Composition and Resting Energy Expenditure Following Weight Loss (Hron et al., 2015)
I think study was actually done a few years ago, originally published here (blogged about here), and re-analyzed through the eyes of Chris Gardner. I think. (But it doesn’t really matter as the study design appears to be identical.)
Experiment: give someone an oral glucose tolerance test (75 grams glucose) and measure insulin 30 minutes later. Some people secrete more insulin than others (a marker of insulin resistance); these people also have a lower metabolic rate after weight loss = increased propensity for weight regain. However, if these people follow a low carbohydrate diet, then the reduction in metabolic rate is attenuated. Some people who don’t secrete a lot of insulin after a glucose load may do better in the long-run with a lower fat diet.