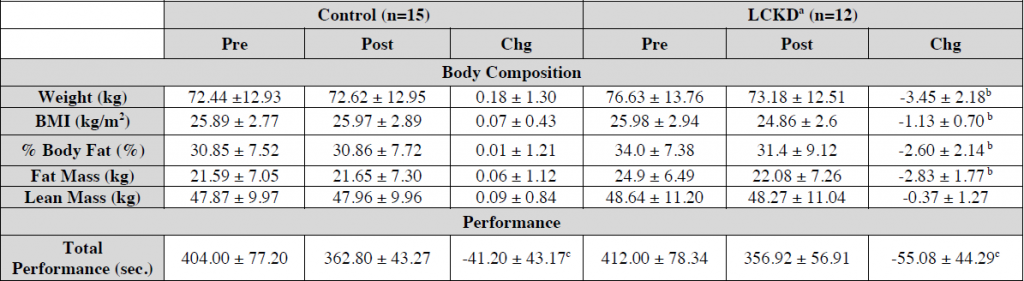
Study: a handful of average-bodied Crossfitters in their mid-30’s were recruited and told to either: 1) keep doing what they’re doing; or 2) go full keto. Crossfit 4x/week. Strength testing before and after 6 weeks (Gregory et al., 2017).
I’ll start with the best part: KETOADAPTATION IS A REAL TRUE THING THAT WORKS (P<0.05). Otherwise, this group’s performance would’ve plummeted. It is known.
The performance test was time to complete a 500-meter row, 40 body weight squats, 30 abdominal mat sit-ups, 20 hand release pushups, and 10 pull-ups.
Tl;dr: both groups knocked about a half a minute off their time!
The key here is duration: 6 weeks of ketogenic dieting is adequate to restore performance back to baseline. <3 weeks is not.
Here’s the downside (sort of):
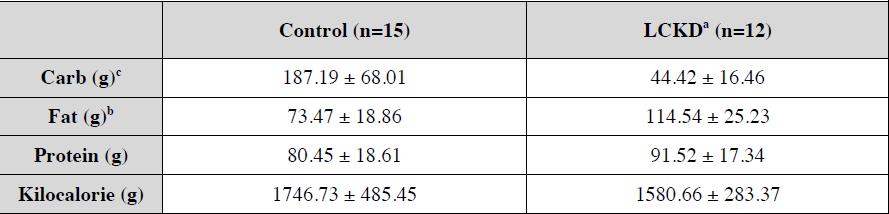
Basically, the keto group dropped carbs and failed to compensate by upping other calories. I know I know, spontaneous ad lib appetite reduction, but this is a study on PHYSICAL PERFORMANCE.
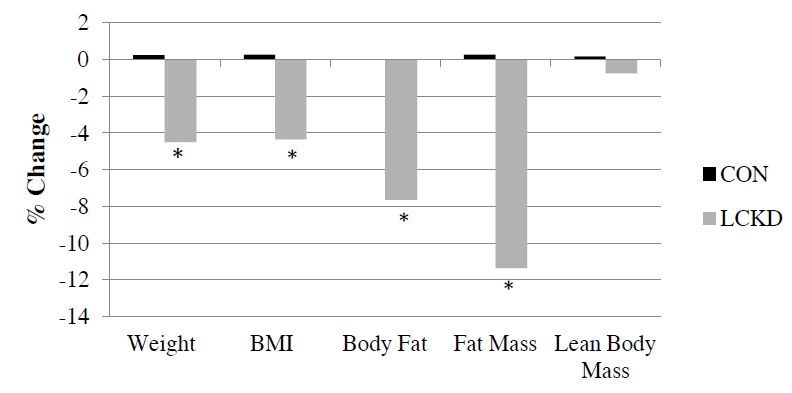
And in further support of “muscle growth sans carbs,” keto dieters upped protein by 15% and this still wasn’t enough to compensate for the reduction in carbs/insulin: they still lost a bit of lean mass (NS). Imagine if they hadn’t increased the brotein? yikes
so basically, they lost body fat because CICO and retained lean mass because exercise and protein haha jk
Admittedly, it was cool to see the body comp changes, but we know fat loss eventually plateaus and people start eating maintenance calories again (maybe a bit more if Ebbeling can be believed). And this is where they remain for the rest of their lives (hopefully). So at 6 weeks, they were still losing weight, nowhere near where they’re going to be for the rest of their lives, but THAT’s where I’d like to see performance testing (ie, at a stable body weight). Don’t get me wrong, I hate myself in advance for making this critique: the researchers should’ve pushed more calories in the keto dieters bc this is a confounder in a study on PHYSICAL PERFORMANCE… but this doesn’t really matter in the big scheme of things because Blackburn’s group did that and showed the results were the same haha
On another note, I don’t think people should expect an additional performance boost from being more ketoadapted (or more fat-adapted or whatever), primarily because whether the study is 3 weeks or 6, performance never really gets better than baseline in experienced athletes. With more advanced training techniques, sure (and I think this is common), but not more keto- or fat-adaptation.
For full access to all articles and much more (or if you just like what I do and want to support it), become a Patron! It’s three bucks a month and there are many other options. Sign up soon because there are only a limited number of spots left at the $3 level. It’s ad-free and you can cancel if it sucks ????
Also, I’m open to suggestions, so please don’t hesitate to leave a comment or contact me directly at drlagakos@gmail.com.
Affiliate discounts: if you’re still looking for a pair of hot blue blockers, Carbonshade is offering 15% off with the coupon code LAGAKOS and Spectra479 is offering 15% off HERE. TrueDark is running a pretty big sale HERE. If you have no idea what I’m talking about, read this then this.
20% off some delish stocks and broths from Kettle and Fire HERE.
If you want the benefits of ‘shrooms but don’t like eating them, Real Mushrooms makes great extracts. 10% off with coupon code LAGAKOS.
calories proper
Become a Patron!