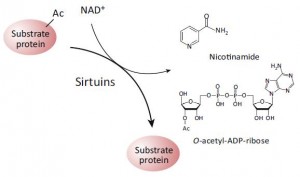
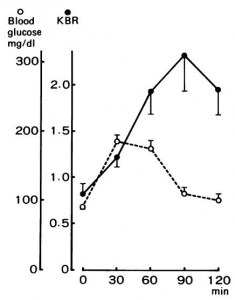
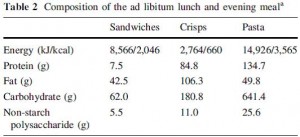
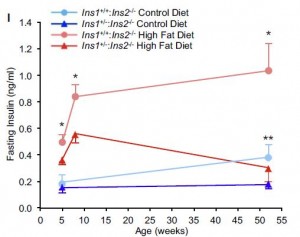
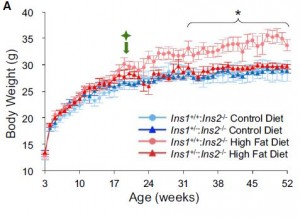
From the best I can gather, one of the more immediate players in circadian biology is the coenzyme nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD), which participates in a variety of redox reactions. Fasting increases the intracellular NAD/NADH ratio, setting off a cascade of events involving epigenetics and the regulation of metabolism.
NAD activates sirtuins, a family of deacetylase enzymes. This is epigenetics.
SIRT1 regulates the activity of BMAL1 and CLOCK, two circadian transcription factors, which target NAMPT, an enzyme that synthesizes NAD. And in a curious feed-forward mechanism, CLOCK and BMAL1 enhance SIRT1 expression… genetic deletion of any of these players induces insulin resistance (Zhou et al., 2014), and this can be recapitulated with constant darkness: reduced BMAL1 and SIRT1, hepatic insulin resistance; the latter can be reversed with resveratrol (which may or may not be acting through SIRT1; this is controversial). While alcohol does no great favors for circadian biology, if you’re going to imbibe, perhaps a resveratrol-rich Argentinian malbec served, and this might be the important part, at night, when all of this stuff is going on… coincidentally [fortunately], that’s precisely when most choose to imbibe.