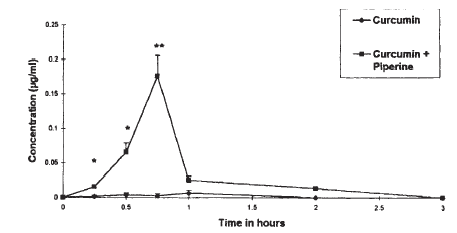
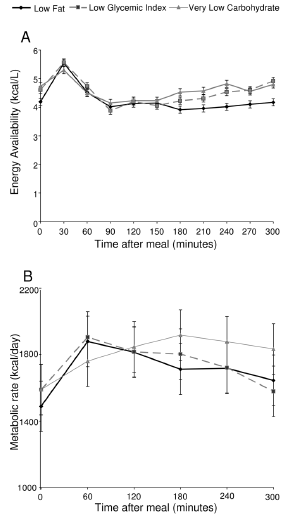
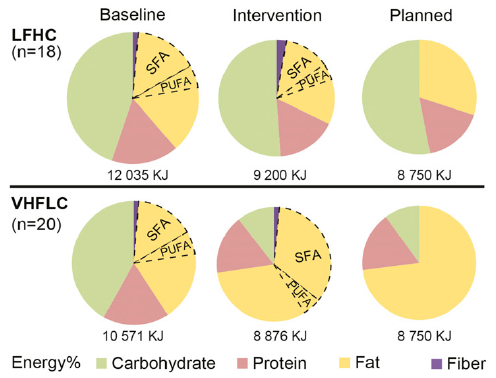
Artificial light at night, crappy sleep, and skipping breakfast are major contributors to poor circadian rhythms. Some bro’s insist WHAT you eat is infinitely more important than WHEN you eat. I beg to differ, at least in part – nix the refined & processed foods and it doesn’t really matter if you prefer low fat or low carb (P<0.05). Evidence: Hunger-free diet(s).
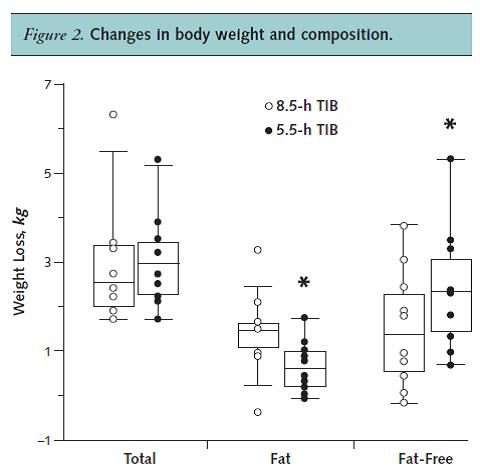
Exhibit A. On the other hand, feed two people identical diets but induce circadian disruption in one and whammo – big difference in outcome.
Significantly less fat loss and more muscle loss in the circadian disrupted group.
Interindividual variability? Yes. Statistical significance? YES.