…but it isn’t dead, imo, because that would be really hard to do. Like, seriously.
Wait, which “insulin hypothesis” was falsified? pic.twitter.com/31pOP9B6Ff
— Bill Lagakos (@CaloriesProper) May 11, 2016
side note: please consider the modern views of Taubes, Lustig, Gardner, Attia, and others on Carbs™. They’re less “Carbs-cause-obesity, keto-for-all, etc.,” and more thinking it might not be Carbs™ per se, but rather processed and refined foods. And #context… And I tend to agree at the moment (nuances and caveats are subject to change, as more evidence accumulates).
disclaimer: I haven’t seen the full text of Hall’s recent study, but that’s not really relevant to what I want to discuss. In other words, I don’t think the full text will provide any additional details on this particular point.
Tl;dr: this study was not designed to prove or disprove metabolic advantage or the insulin-obesity hypothesis.
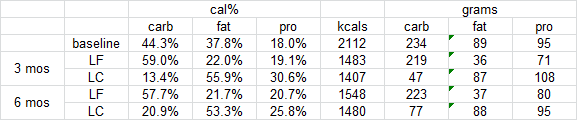
It’s in the study design: four weeks of low fat followed by four weeks of low carb. We KNOW that weight loss slows over time (especially if calories are controlled, as they were in this study). It has to do with the order of treatments.
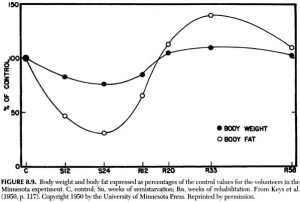
Weight loss-slowing over time in the Minnesota Experiment: