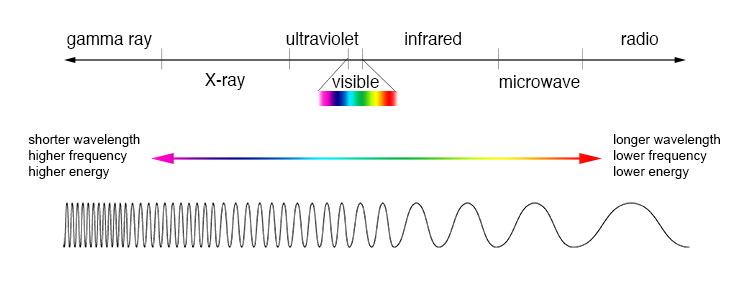
Check out the above image of the electromagnetic (EM) spectrum. Different biohacking eyewear have different purposes, and it largely depends where on the EM spectrum they act.
If you stare at a computer screen (or iPad, smart phone, etc., etc.) all day, the specialized glasses you may want to look into block out light just south of the visible light wavelengths. These will help with eye strain, headaches, etc. You could use bona fide blue blockers for this, as they block blue and everything south, although it’d be overkill and probably annoying due to visual disturbance. Pixels and Gunnars are good for this, but they’re not especially great at blocking blue light (with the possible exception of the amber-tinted Gunnars).
Warning: there’s an article floating around on the internet saying it’s useless to block blue light because those computer glasses don’t preserve melatonin secretion. This is a STRAWMAN. Computer glasses aren’t designed to block blue light.
The truth: it’s still important to block blue light at night. If you get eye strain or headaches staring at a computer screen, than computer glasses may be appropriate.
Blocking blue light at night is key for proper melatonin secretion and preservation of circadian rhythms.
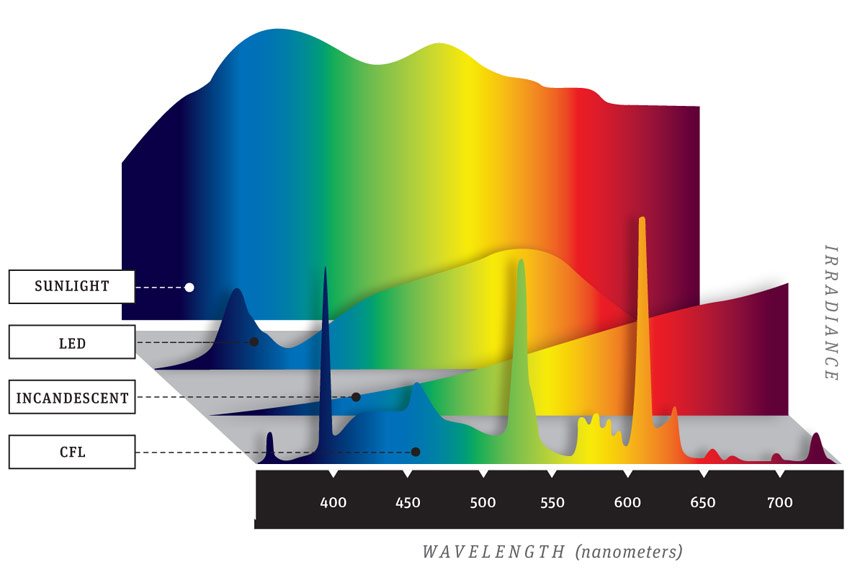
Most smart devices emit LED light which has a particular spike in the blue range:
If you need to light at night: moonlight or candles > amber or red-tinted bulbs > low watt incandescent bulb. They should be positioned below eye level as light entering the eyes from above more effectively suppresses melatonin than light from below (with the exception of moonlight LOL) (Glickman et al., 2003).
Amber lenses to block blue light and improve sleep: a randomized trial (Burkhart and Phelps, 2009)
Wearing blue light-blocking glasses in the evening advances circadian rhythms in the patients with delayed sleep phase disorder: an open-label trial (Esaki et al., 2016)
Uvex Skypers … Gunnars … Carbonshades (probably the most effective blue blockers available) … Solar Shields … BLUblox (less expensive and pretty cool-looking, too) … Spectra479
Spectra479 and Carbonshade are offering a 15% discount with the coupon code LAGAKOS!
Circadian misalignment augments markers of insulin resistance and inflammation independently of sleep loss (Leproult et al., 2014)
For the rest of this article or if you just want to support the show, head over to Patreon!
Three bucks a month for access to all articles and there are many other options. And it’s ad-free.
If you’re on the fence considering it, try it out, you can cancel at any time! Also, there is a limited number of positions remaining at the $3 level.
Lastly, I’m open to suggestions; please feel free leave a comment or email me directly at drlagakos@gmail.com.