Fruits and veggies, fermented or otherwise, aren’t the only source of prebiotics in your diet. Eat a whole sardine and some of the ligaments, tendons, bones, and cartilage will surely escape digestion to reach the distal intestine where they will be fermented by the resident microbes.

Salmon skin and the collagen in its flesh, the tendons that hold rib meat to the bone, and maybe even some of the ligaments between chicken bones. All of these are potential prebiotics or “animal fibres.” And it may explain why fermented sausages are such good vessels for probiotics.
“Animal prebiotic” may be a more appropriate term because the food matrix is quite different from that of non-digestible plant polysaccharides. And while I doubt those following carnivorous diets are dining exclusively on steak, these studies suggest it might be particularly important to eat a variety of animal products (as well as greens, nuts, dark chocolate, fermented foods, etc.) in order to optimize gut health.

These studies are about the prebiotics in a cheetah’s diet. Cheetah’s are carnivores, and as such, they dine on rabbits, not rabbit food.

As somewhat of a proof of concept study, Depauw and colleagues tried fermenting a variety of relatively non-digestible animal parts with cheetah fecal microbes (2012). Many of the substrates are things that are likely present in our diet (whether we know it or not).
Cartilage
Collagen (tendons, ligaments, skin, cartilage, bones, etc.)
(tendons, ligaments, skin, cartilage, bones, etc.)
Glucosamine-chondroitin (cartilage)
(cartilage)
Glucosamine (chitin
(chitin from shrimp exoskeleton? exo bars made with cricket flour?)
from shrimp exoskeleton? exo bars made with cricket flour?)
Rabbit bone, hair, and skin (Chicken McNuggets?)
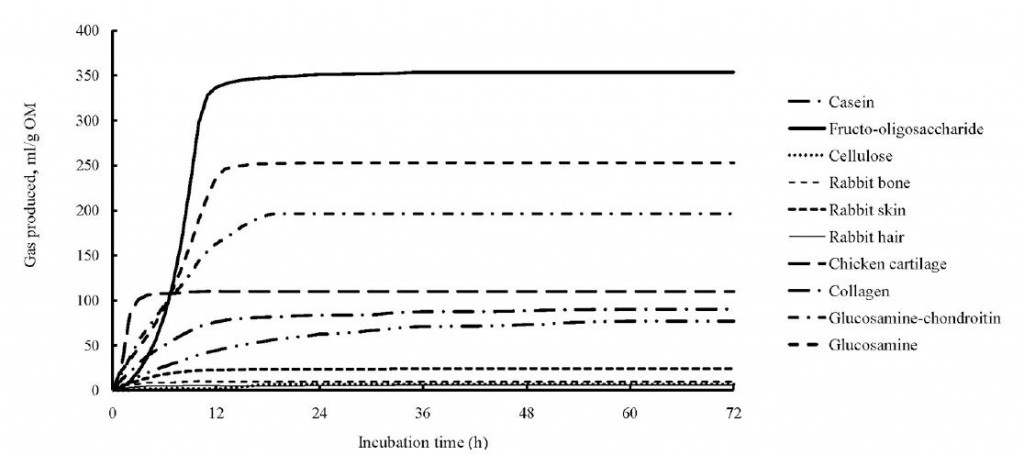
The positive control, fructooligosaccharides (FOS) , was clearly the most fermentable substrate; however, glucosamine and chondroitin weren’t too far behind. Chicken cartilage and collagen were also well above the negative control (cellulose). Rabbit skin, hair, and bone weren’t particularly good substrates.
, was clearly the most fermentable substrate; however, glucosamine and chondroitin weren’t too far behind. Chicken cartilage and collagen were also well above the negative control (cellulose). Rabbit skin, hair, and bone weren’t particularly good substrates.
As to fermentation products, collagen, glucosamine, and chondroitin were actually on par with FOS in terms of butyrate production:
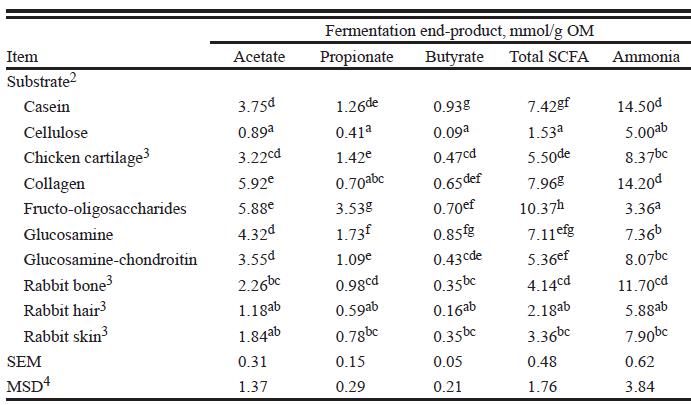
Glycosaminoglycans (glucosamine and chondroitin) are found in cartilage and connective tissues (ligaments and tendons) and may have been mediating some of these effects as they’re some of the carbiest parts of animal products. Duck Dodgers wrote about this in a guest post at FTA and in the comments of Norm Robillard’s article (probably elsewhere, too); very interesting stuff.
The authors also mentioned that the different fermentation rates in the first few hours suggests an adaptive component (some took a while to get going), or that certain substrates induced the proliferation of specific microbes. “Animal prebiotics.”
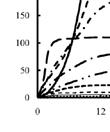
This is particularly noticeable for FOS (solid line), which is a plant fibre that wouldn’t really be present at high levels in a cheetah’s diet, so the microbes necessary to ferment it were probably not very abundant (initially). Chicken cartilage (long dashes), on the other hand, started immediately rapidly fermenting, perhaps because this is more abundant in the cheetah’s diet.
Depauw took this a step further and fed cheetahs either exclusively beef or whole rabbit for a month (2013). Presumably, the beef had much less animal fibre than whole rabbit. When they initially examined fecal short chain fatty acids, there were no major differences between the groups:
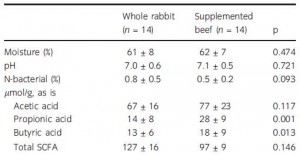
However, if you take into consideration that the whole rabbit-fed cheetahs produced over 50% more crap than meat-fed cheetahs, then some other differences become apparent. For example, the concentration of total SCFAs is actually greater in the feces from whole rabbit-fed cheetahs:
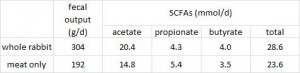
edit: la Frite pointed out that the table in the original manuscript is incorrect; the total SCFA numbers are reversed. The excel table above is corrected.
Further, the mere fact that there was 50% more fecal mass per day pretty much confirms way more animal fibre in whole rabbits. And while neither of these studies were accompanied by microbial analysis, a more recent study on cheetahs fed primarily meat, “randomly interspersed with unsupplemented whole rabbits,” showed low levels of Bacteroidetes and Bifidobacteria , two potentially health-promoting groups of microbes (Becker et al., 2014). I suspect this may have been at least partially due to a relative lack of animal fibre, compared to the Depauw’s exclusive whole rabbit diet.
, two potentially health-promoting groups of microbes (Becker et al., 2014). I suspect this may have been at least partially due to a relative lack of animal fibre, compared to the Depauw’s exclusive whole rabbit diet.
Human digestive physiology and gut microbes are certainly far different from that of a cheetah, but maybe we too receive some prebiotic benefits from these animal fibres… just something to think about next time you’re eating sardines or pork ribs.
Consults are open, contact me if you’re interested: drlagakos@gmail.com
Affiliate links: Still looking for a pair of hot blue blockers? TrueDark is offering 10% off HERE and Spectra479 is offering 15% off HERE. If you have no idea what I’m talking about, read this then this.
Join Binance and get some cryptoassets or download Honeyminer and get some Bitcoins for free!
20% off some delish stocks and broths from Kettle and Fire HERE.
If you want the benefits of ‘shrooms but don’t like eating them, Real Mushrooms makes great extracts. 10% off with coupon code LAGAKOS. I recommend Lion’s Mane for the brain and Reishi for everything else.
Join Earn.com with this link.
Start your OWN Patreon campaign!
calories proper
Become a Patron!
may have missed some of the nuances here.